How Seasonal Changes Affect Solar Panels and the Grid
- 1.Solar Panel Technologies: Unveiling the Power of the Sun
- 2.Overcoming Challenges: Navigating the Complexities of Connecting Solar to the Grid
- 3.Top 10 Weirdest Innovations in Solar Energy Technology
- 4.Once You’ve Decided to Go Solar: What Are the Next Steps and What to Expect?
- 5.The Comprehensive Benefits of Adding Solar to Your Home or Business
- 6.The Impact of Solar Energy on Property Value: How Installing Solar Panels Can Boost Residential and Commercial Real Estate
- 7.How to Make Sure Your House or Office Building is in Top Shape and Ready for Solar Energy
- 8.How Seasonal Changes Affect Solar Panels and the Grid
- 9.New Year, New Energy: Why 2025 Is the Perfect Year to Go Solar
- 10.Keeping the Lights On: How Solar Energy Shields You from Power Outages
- 11.Top Solar Technology Trends to Watch in 2025
- 12.Spring into Savings: Why Now is the Best Time to Go Solar in Puerto Rico
- 13.Understanding the Process of Connecting Solar to the Grid: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 14.Solar and Gardening: Can Panels and Plants Coexist?
- 15.Summer Energy Savings: How Solar Power Can Lower Your Utility Bills This Summer
As the seasons change, so does the amount of sunlight reaching solar panels, affecting their performance and the overall energy production. From long summer days to the shorter, cloudier days of winter, these changes can impact how much energy solar systems generate. Understanding how seasonal shifts affect solar panels and the grid can help homeowners and businesses better prepare for energy fluctuations, optimize usage, and manage their systems efficiently.
Solar Power Generation: How Weather and Seasonality Impact Performance
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells. The amount of sunlight a panel receives depends on the time of day, geographical location, and weather conditions. Seasonal changes, particularly the angle and duration of sunlight, play a significant role in energy production.
- Summer – Maximizing Energy Production
Summer is typically the best season for solar energy generation. Longer days and higher sun angles mean more sunlight throughout the day, resulting in higher energy production. Solar panels are most efficient when exposed to direct sunlight, which is abundant in summer. The increased daylight hours also allow for longer periods of energy production.
However, excessive heat can reduce panel efficiency. Solar panels work best at cooler temperatures, and heat can cause them to be less efficient at converting sunlight. Though heat does not have a dramatic impact on summer performance, it’s important to monitor your system for optimal efficiency.
- Fall – Gradual Decline in Sunlight
In the fall, days grow shorter, and the sun’s angle decreases. The reduced amount of sunlight means solar panels generate less energy than in the summer. However, the transition is gradual, and mild, sunny weather in fall can still allow solar systems to function efficiently. This is a good time to monitor your energy use and adjust for the coming winter months.
- Winter – Shorter Days and Cloudier Skies
Winter presents some of the most significant challenges for solar energy generation. Shorter days and a lower sun angle mean solar panels receive less sunlight. In many regions, winter also brings overcast skies and storms, further reducing solar power output. Despite this, solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, though at lower levels. Energy storage systems can be useful during this time, storing power for use when solar generation is low.
Snow can also affect performance, as it may cover the panels and block sunlight. While most panels are designed to shed snow, it’s still advisable to check the system after heavy snowfalls to maintain performance.
- Spring – A Time for Rejuvenation
Spring sees a rise in solar power production as days lengthen and the sun climbs higher in the sky. With more sunlight available, solar panels begin generating more electricity. This is a good time to clean and inspect your solar panels to ensure optimal performance for the upcoming summer months.
How Seasonal Changes Affect the Grid
Solar energy plays an important role in the electrical grid, especially in regions where it makes up a significant portion of energy production. Understanding how solar energy generation fluctuates with the seasons helps grid operators ensure a consistent power supply year-round.
- Seasonal Imbalances
The amount of solar energy generated varies significantly by season. During summer, solar generation is at its peak, reducing the strain on the grid, especially in hot regions where air conditioning use increases. However, in winter, when solar generation decreases, the grid may rely more heavily on other energy sources like natural gas or coal. Managing this imbalance is essential for grid operators to maintain stability.
- Energy Storage Solutions
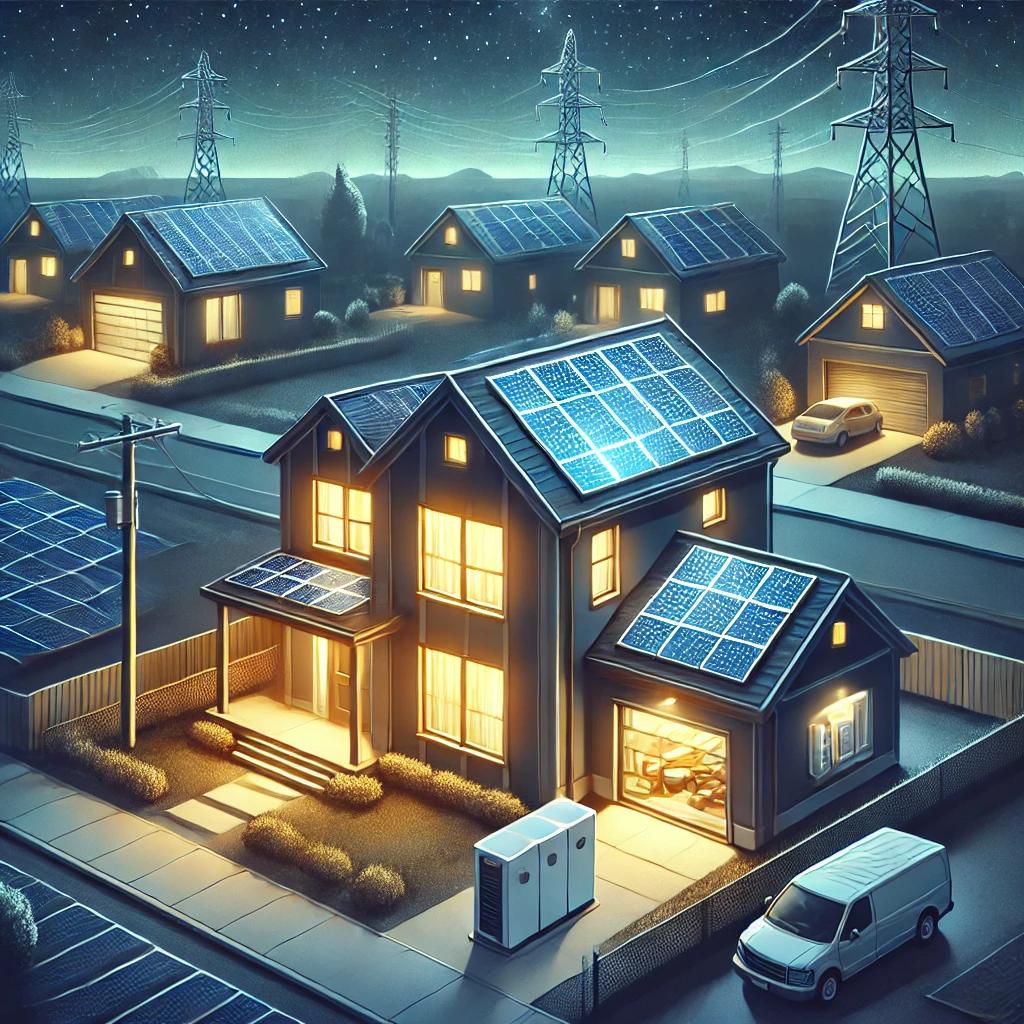
Energy storage, such as batteries, helps balance the fluctuations in solar power. By storing excess energy during sunny periods, these systems can provide power during times of low solar generation, like at night or in winter. For homeowners and businesses, battery storage can help ensure a continuous energy supply, even when the sun isn’t shining.
- Grid Integration and Smart Grids
As solar energy becomes more prevalent, the grid is evolving to accommodate these changes. Smart grids use advanced technology to optimize the distribution of electricity, adjusting in real-time to fluctuations in solar power generation. These grids can direct power to areas with high demand and store excess energy for later use. Additionally, microgrids, which are localized energy systems, can operate independently from the main grid and provide resilience during power outages, such as those caused by winter storms.
Final Thoughts
While seasonal changes affect the amount of energy generated by solar panels, the impact is not drastic. With the right preparations, such as energy storage and understanding seasonal patterns, solar energy can remain a reliable power source throughout the year. As solar technology continues to advance and the grid adapts to renewable energy, solar systems will become even more efficient and stable, no matter the season.
For more information on how to optimize your solar panel system and prepare for seasonal changes, contact us at MFS Solar. Our team of experts is here to help you maximize your energy production and savings all year long. Reach out today to get started!