Top 10 Weirdest Innovations in Solar Energy Technology
- 1.Solar Panel Technologies: Unveiling the Power of the Sun
- 2.Overcoming Challenges: Navigating the Complexities of Connecting Solar to the Grid
- 3.Top 10 Weirdest Innovations in Solar Energy Technology
- 4.Once You’ve Decided to Go Solar: What Are the Next Steps and What to Expect?
- 5.The Comprehensive Benefits of Adding Solar to Your Home or Business
- 6.The Impact of Solar Energy on Property Value: How Installing Solar Panels Can Boost Residential and Commercial Real Estate
- 7.How to Make Sure Your House or Office Building is in Top Shape and Ready for Solar Energy
- 8.How Seasonal Changes Affect Solar Panels and the Grid
- 9.New Year, New Energy: Why 2025 Is the Perfect Year to Go Solar
- 10.Keeping the Lights On: How Solar Energy Shields You from Power Outages
- 11.Top Solar Technology Trends to Watch in 2025
- 12.Spring into Savings: Why Now is the Best Time to Go Solar in Puerto Rico
- 13.Understanding the Process of Connecting Solar to the Grid: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 14.Solar and Gardening: Can Panels and Plants Coexist?
- 15.Summer Energy Savings: How Solar Power Can Lower Your Utility Bills This Summer
- 16.What Is Ground-Mounted Solar? A Complete Guide for Homeowners & Businesses
- 17.How Much Electricity Does Your Business Need to Go Solar?
- 18.Why Fall is the Best Time to Install Solar Panels
Solar energy panels, while primarily seen as a sustainable energy solution, have some interesting and unusual aspects. Here are ten of the weirdest things about solar energy panels:
- Solar Panel Roads: Some countries have experimented with embedding solar panels into roads to generate electricity from traffic. For example, the “Wattway” project in France installed solar panels on a one kilometer stretch of road, though these projects face challenges like durability and efficiency.
- Solar Panel Art: Solar panels can be integrated into artistic installations and architecture. For instance, solar trees and solar sculptures combine aesthetic appeal with functionality, creating public art that also generates renewable energy.
- Solar Skin: New technologies allow for customizable solar panels that blend in with building materials. “Solar skin” technology can make solar panels resemble traditional roofing materials, murals, or even camouflage patterns, making them more visually appealing.
- Solar-Powered Desalination: Solar energy is used to power desalination plants that turn seawater into drinkable water. This application is particularly useful in arid regions where freshwater is scarce, but sunlight is abundant.
- Agrivoltaics: Combining agriculture and solar energy production, agrivoltaics involves installing solar panels above crops. This dual-use approach can increase land efficiency, providing shade for crops while generating electricity.
- Floating Solar Farms: Solar panels can be installed on bodies of water, such as lakes and reservoirs. These floating solar farms can reduce water evaporation and algae growth while generating electricity without using valuable land space.
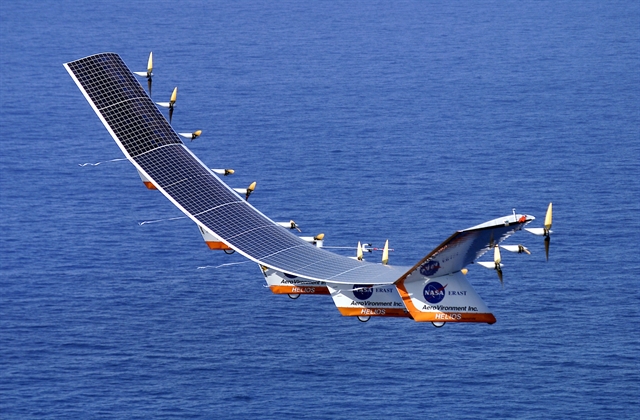
- Solar-Powered Planes: Solar-powered aircraft, like the Solar Impulse, can fly long distances using only solar energy. Solar Impulse 2, for example, completed a circumnavigation of the globe without using any fuel.
- Solar Panel Recycling: As solar panels reach the end of their lifespan, recycling them presents a unique challenge. Companies are developing methods to reclaim valuable materials from old panels, such as silicon, silver, and aluminum, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Solar panels can be integrated directly into building materials, such as windows, facades, and roof tiles. This not only saves space but also turns entire buildings into power generators.
- Solar-Powered Fabric: Researchers are developing solar textiles that can be woven into clothing. These fabrics contain tiny solar cells, allowing people to charge their devices on the go using energy harvested from their clothes.
So, whether you’re strutting down the street in your solar-powered jacket, driving on a sun-soaked highway, or enjoying a quiet day on a floating solar farm, remember: the future of solar energy is bright, bizarre, and just a bit bonkers. And who knows? Maybe one day you’ll be sipping solar-powered desalinated water while admiring a solar panel art installation on your neighbor’s roof—all while charging your phone from your pants.
The sun sure knows how to keep things interesting!